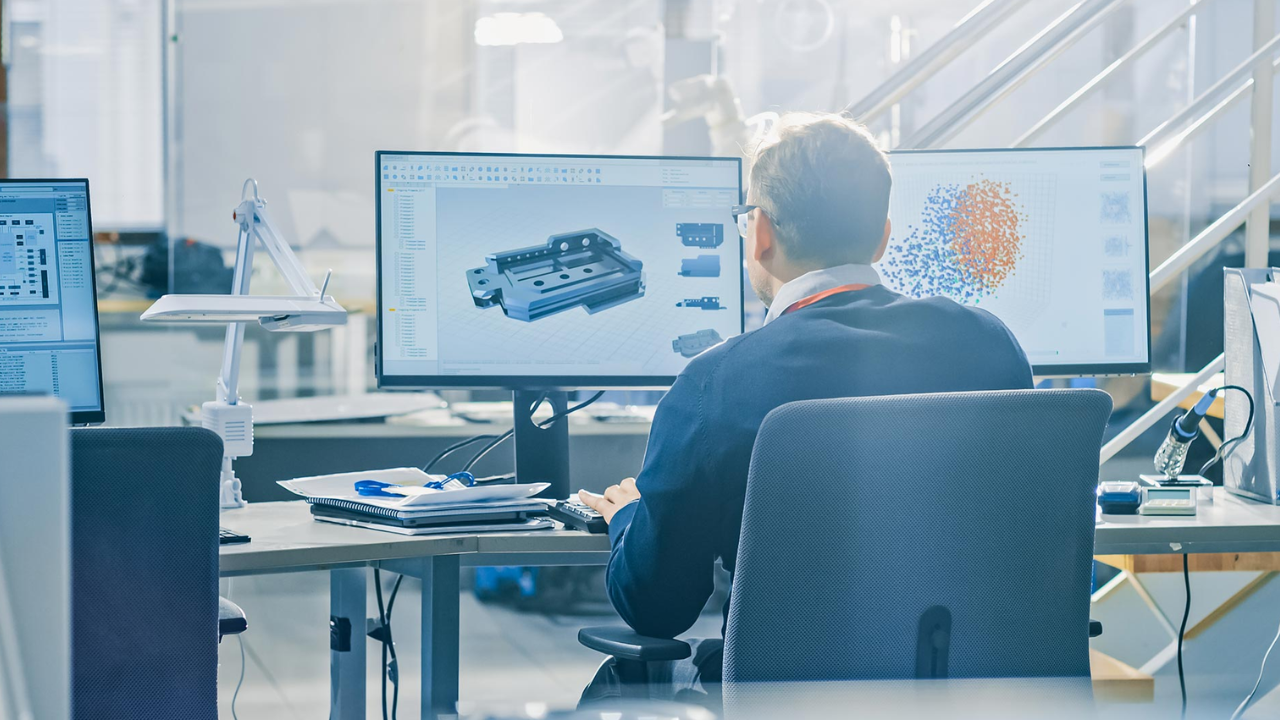
Modern products are becoming increasingly complex, boasting advanced features and functionalities. While this complexity offers many advantages for consumers, it also presents significant challenges for manufacturers.
Ensuring that these intricate products can be manufactured efficiently and cost-effectively necessitates a strategic approach. Enter Design Manufacturability (Design for Manufacturability) – a powerful methodology that bridges the gap between the design and manufacturing processes.
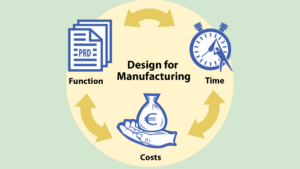
What is Design Manufacturability?
Design Manufacturability, often abbreviated as DfM, is a proactive and collaborative approach that integrates manufacturing considerations directly into the design phase of a product. By meticulously analyzing factors like material selection, part complexity, and assembly processes from the outset, Design Manufacturability fosters the creation of products that are not only innovative and functional but also optimized for smooth and cost-effective production.
This shift in focus, from designing a product in isolation to considering its manufacturability from the beginning, offers a multitude of benefits for manufacturers. In the next part, we’ll delve deeper into the value proposition of Design Manufacturability in today’s engineering landscape.
The Value of Design Manufacturability in Today’s Engineering Landscape
Today even the slightest edge can translate into significant success. Design Manufacturability (DfM) empowers engineers to gain that edge by fostering a more holistic and efficient approach to product development. Here’s how DfM benefits engineers and the overall engineering landscape:
- Reduced Development Time and Costs: By identifying and addressing potential manufacturability challenges during the design phase, DfM helps eliminate costly rework and production delays later in the process. This streamlined approach translates into faster development times and reduces overall project costs.
- Enhanced Product Quality and Functionality: DfM encourages the selection of materials and processes that are well-suited for the intended function of the product. This focus on manufacturability often leads to more robust designs with fewer potential failure points, ultimately resulting in higher quality products. Additionally, DfM principles can sometimes lead to innovative design solutions that enhance the overall functionality of the product.
- Improved Time-to-Market: The streamlined production processes facilitated by DfM enable manufacturers to bring products to market faster. By eliminating bottlenecks and ensuring a smooth transition from design to production, DfM helps businesses capitalize on emerging market opportunities and maintain a competitive edge.
- Stronger Collaboration Between Design and Manufacturing Teams: DfM fosters a collaborative environment where design and manufacturing teams work together from the beginning of the product development process. This open communication and shared understanding of design goals and manufacturing constraints lead to more efficient product development and a more positive working environment.
The Role of the Design Manufacturability Engineer
With the growing importance of DfM, the role of the Design Manufacturability engineer (DfM engineer) has become increasingly crucial. These specialized engineers act as a bridge between the design and manufacturing teams, ensuring that manufacturability considerations are seamlessly integrated into the product development process.
DfM engineers possess a unique skillset that blends engineering expertise with a deep understanding of manufacturing processes and limitations. They are responsible for analyzing designs, identifying potential manufacturability challenges, and proposing solutions that optimize production efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Design Manufacturability in Action: Practical Considerations for Engineers
Successfully integrating Design Manufacturability (DfM) principles into your engineering workflow empowers you to create products that are not only innovative but also manufacturable at scale. Here are some actionable steps you can take:
- Early Consideration of Design Manufacturability: Don’t wait until the later stages of design to consider manufacturability. Integrate DfM principles from the very beginning of the design process. This allows you to identify and address potential challenges early on, minimizing costly rework and delays.
- Utilizing Design Manufacturability Software and Tools: A variety of Design Manufacturability software and tools are available to assist engineers in analyzing designs and identifying potential manufacturability issues. These tools can simulate production processes, assess part complexity, and recommend alternative materials or techniques to optimize manufacturability.
- Collaboration is Key: Effective communication and collaboration between design and manufacturing teams are essential for successful DfM implementation. Regularly engage with manufacturing personnel to gain insights into their capabilities and limitations. This collaborative approach fosters a shared understanding of design goals and manufacturing constraints, leading to more efficient product development.
- Standardization and Simplification: Whenever possible, strive for standardization and simplification in your designs. Utilizing readily available standard components and minimizing part complexity can significantly reduce manufacturing costs and improve assembly efficiency.
- Design for Automation: Consider the potential for automating various aspects of the production process during the design phase. Designing products that are compatible with automated equipment can streamline production, reduce labor costs, and increase overall production throughput.
- Continuous Learning: The field of Design Manufacturability is constantly evolving with advancements in technology and manufacturing techniques. Stay up to date on the latest DfM best practices and emerging technologies by attending workshops, conferences, and participating in industry communities.
Conclusion:
Design Manufacturability (DfM) is a powerful and strategic approach that empowers engineers to bridge the gap between design and manufacturing. By integrating DfM principles throughout the product development process, engineers can create high-quality, functional products that are also cost-effective to manufacture. At MARS, we understand the critical role of Design Manufacturability in achieving success in today’s competitive manufacturing landscape. We are committed to fostering collaboration and innovation throughout the product development cycle, ensuring that our products are not only cutting-edge but also efficiently manufactured.
Ready to explore how design can benefit your manufacturability for your engineering projects? We’re just a call away!