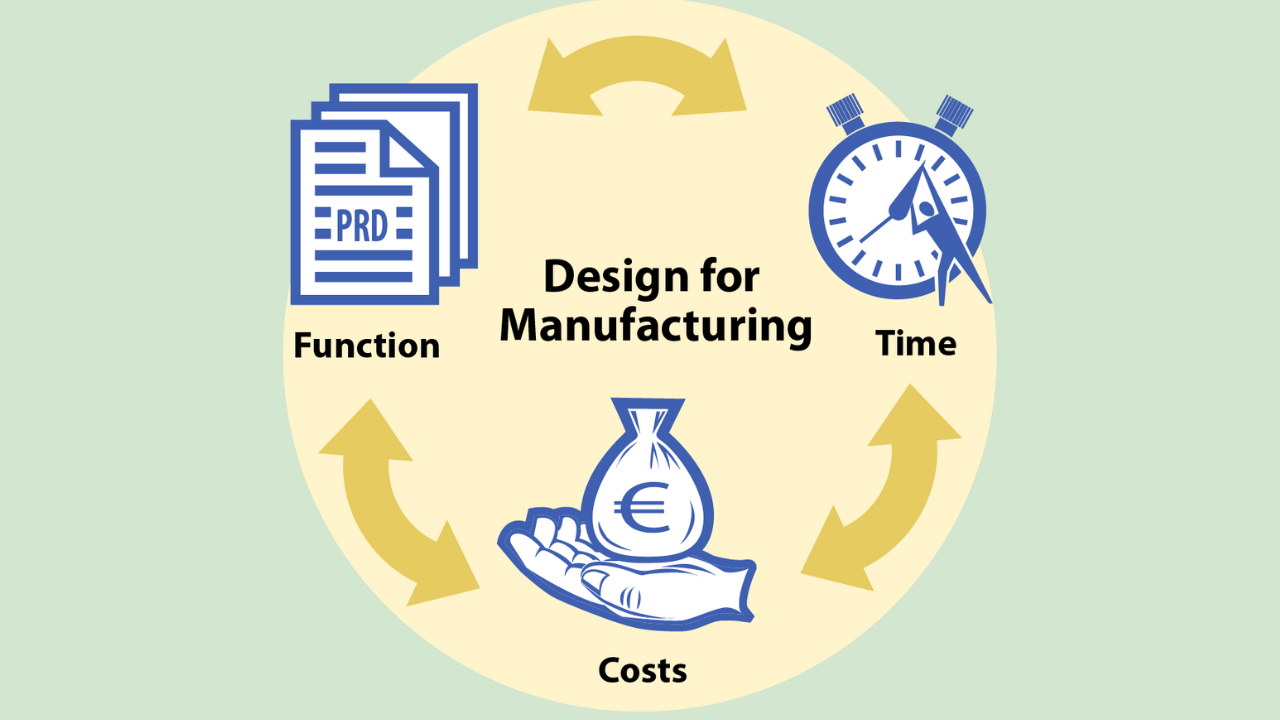
Manufacturers face relentless pressure to optimize costs, elevate product quality, and accelerate time-to-market. In this competitive environment, even the slightest edge can translate into significant success.
Enter DfMA (Design for Manufacture and Assembly). This strategic approach empowers manufacturers to achieve these goals by integrating manufacturing and assembly considerations directly into the design phase. By proactively addressing manufacturability and assembly challenges during the design stage, DfMA unlocks a range of benefits that streamline production, enhance product quality, and ultimately propel manufacturers towards long-term success.
What is DfMA?
DfMA full form is Design for Manufacture and Assembly. It’s a comprehensive methodology that encourages designers and engineers to consider the entire product lifecycle – from raw materials to final assembly – during the initial design stages. This proactive approach fosters collaboration between design and manufacturing teams, ensuring that products are not only innovative and functional but also cost-effective to manufacture and assemble.
The core principle of DfMA lies in simplifying complexity. By meticulously analyzing factors like part count, material selection, and assembly processes, DfMA helps create products that are easier to manufacture, assemble, and ultimately, maintain. This translates into a multitude of advantages for manufacturers, including:
- Reduced Manufacturing Costs: Fewer parts, simpler processes, and optimized material usage all contribute to significant cost savings.
- Improved Product Quality: Streamlined assembly processes minimize the risk of errors, leading to higher quality products.
- Faster Time-to-Market: By eliminating production bottlenecks and streamlining assembly, DfMA accelerates the process of bringing products to market.
- Enhanced Product Design: DfMA fosters innovation by encouraging designers to explore alternative materials, production techniques, and assembly methods, potentially leading to more functional and user-friendly products.
The Power of DfMA: Simplifying Design for Smoother Production
As discussed earlier, DfMA offers a multitude of advantages for manufacturers. Let’s explore some of the key benefits in greater detail:
1. Reduced Manufacturing Costs: DfMA’s core principle of simplifying complexity directly translates to cost savings. Here’s how:
- Part Reduction: By analyzing the design and identifying opportunities to consolidate parts or eliminate unnecessary components, DfMA minimizes the overall number of parts required for assembly. This not only reduces material costs but also simplifies the procurement process and minimizes inventory management needs.
- Optimized Material Selection: DfMA encourages the selection of materials that are not only cost-effective but also well-suited for the manufacturing process. This can involve considering factors like machinability, formability, and compatibility with existing production equipment. By selecting the right materials, DfMA minimizes material waste and reduces the need for specialized tooling.
- Streamlined Processes: DfMA promotes the design of products that can be manufactured using existing equipment and processes. This eliminates the need for investing in new machinery or developing complex production techniques, ultimately reducing overall manufacturing costs.
2. Improved Product Quality: Streamlined assembly processes facilitated by DfMA directly contribute to enhanced product quality. Here’s why:
- Minimized Assembly Errors: By simplifying assembly procedures and reducing the number of parts, DfMA minimizes the potential for human error during the assembly process. This leads to fewer defects and a higher overall quality of the finished product.
- Enhanced Design for Reliability: DfMA encourages the consideration of potential failure points during the design phase. This proactive approach allows engineers to incorporate design features that mitigate these risks, leading to more reliable and durable products.
3. Faster Time-to-Market: In today’s competitive market, getting products to market quickly is crucial for success. DfMA accelerates this process in several ways:
- Eliminating Production Bottlenecks: By identifying potential manufacturing challenges during the design stage, DfMA helps eliminate bottlenecks that could slow down production. This ensures a smooth transition from design to production, accelerating time-to-market.
- Simplified Assembly Processes: Streamlined assembly procedures facilitated by DfMA reduce the overall time required for product assembly. This allows manufacturers to bring products to market faster and capitalize on emerging market opportunities.
4. Enhanced Product Design: DfMA fosters innovation by encouraging designers to explore alternative materials, production techniques, and assembly methods. This focus on simplification can lead to more creative and user-friendly product designs. Additionally, DfMA promotes the integration of design for manufacturability and serviceability (DFMS) principles. This holistic approach ensures that products are not only easy to manufacture but also simple to service and maintain, enhancing their overall value proposition.
The DfMA Methodology: A Step-by-Step Guide
DfMA is a structured approach that can be integrated seamlessly into the existing design workflow. Here’s a breakdown of the key stages involved in the DfMA methodology:
1. Design for Manufacturability (DFM):
This phase focuses on analyzing the manufacturability of individual parts within the product design. Here’s what it entails:
- Part Analysis: Each part is meticulously evaluated for its manufacturability using factors like:
- Material selection: Considering factors like cost, machinability, availability, and compatibility with existing equipment.
- Part complexity: Analyzing factors like geometric features, tolerances, and potential for simplification.
- Potential for automation: Assessing the suitability of each part for automated manufacturing processes.
- DFM Techniques: Several tools and techniques can be employed during DFM analysis, such as:
- Design for Manufacturing (DFM) software: These software programs assist in analyzing manufacturability by simulating production processes and identifying potential challenges.
- FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis): This technique helps identify potential failure points in the design and implement preventative measures.
- Boothroyd Dewhurst DfMA methodology (optional): This established DfMA framework provides a comprehensive approach to part analysis and cost estimation.
2. Design for Assembly (DFA):
This phase focuses on simplifying the product assembly process. Here’s what it involves:
- Assembly Analysis: The entire assembly process is meticulously evaluated, considering factors like:
- Number of parts: Minimizing the overall number of parts simplifies assembly and reduces the risk of errors.
- Assembly sequence: Identifying the optimal sequence for assembling the various components ensures efficiency and minimizes handling time.
- Ease of assembly: Analyzing the design for factors like accessibility of components and the need for specialized tools during assembly.
- DFA Techniques: Several techniques can be employed during DFA analysis, such as:
- Design for Assembly checklists: These checklists identify best practices for simplifying assembly and minimizing potential issues.
- Poka-Yoke (mistake-proofing) principles: Implementing design features that prevent errors during assembly, such as using specific part shapes that only fit together correctly.
By following these steps and employing the appropriate techniques, DfMA empowers manufacturers to create products that are not only innovative and functional but also cost-effective to manufacture and assemble.
Implementing DfMA: A Practical Guide
Successfully implementing DfMA requires more than just understanding the methodology. Here are some practical steps manufacturers can take:
- Integrating DfMA into the Design Workflow: DfMA principles should be embedded into the entire design process, from initial concept development to final design review. This ensures that manufacturability and assembly considerations are addressed from the outset.
- Collaboration between Design and Manufacturing Teams: Effective communication and collaboration between design and manufacturing teams are crucial for successful DfMA implementation. Early and ongoing communication fosters a shared understanding of design goals and manufacturing constraints.
- Training and Upskilling Employees: Equipping design and manufacturing personnel with the necessary knowledge and skills in DfMA principles is essential. This training can empower them to actively participate in the DfMA process and identify opportunities for improvement.
Conclusion
DfMA is a powerful and versatile approach that empowers manufacturers to achieve significant competitive advantages. By strategically integrating DfMA principles into the design process, manufacturers can streamline production, reduce costs, enhance product quality, and accelerate time-to-market. At MARS, we are committed to innovation and fostering efficient manufacturing practices. We understand the importance of DfMA and actively collaborate with our partners to implement these principles throughout the product development cycle.
If you’re interested in learning more about how DfMA can benefit your manufacturing operations, we encourage you to get in touch with our team of experts.